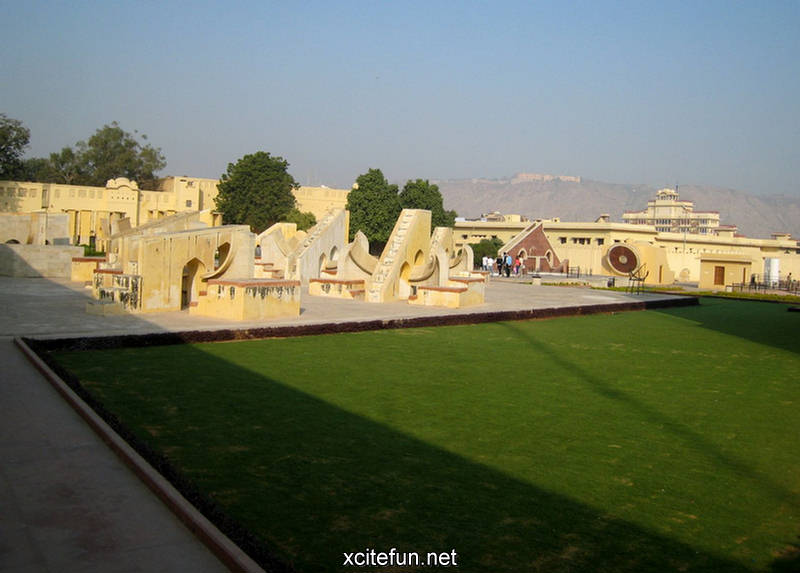
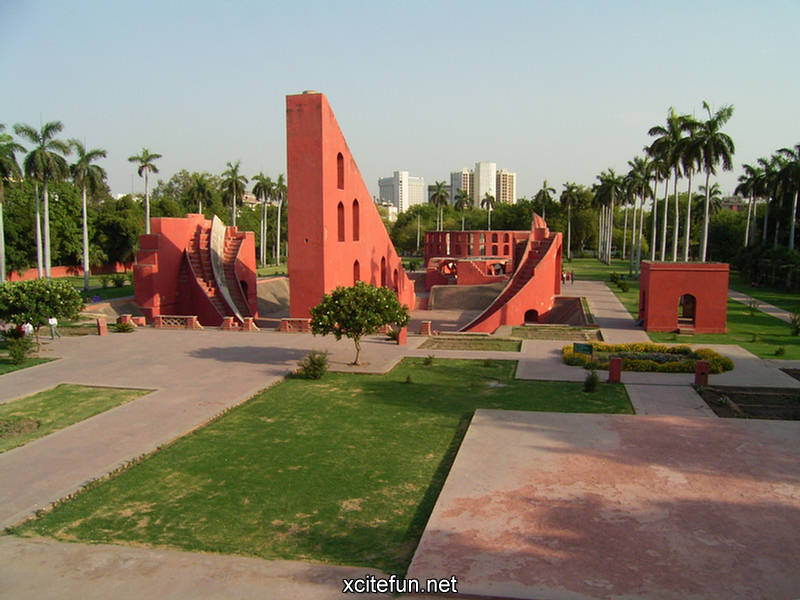
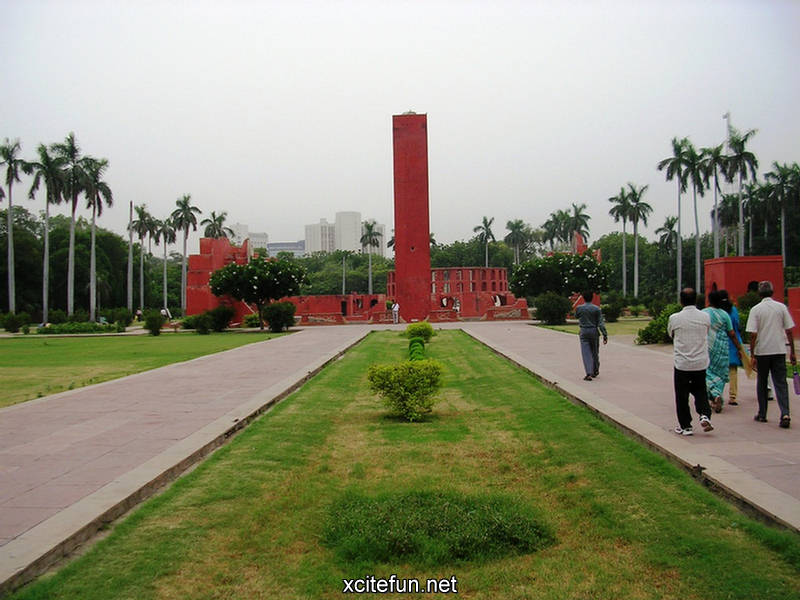
Jantar Mantar Astronomy Park - Scientific Heritage
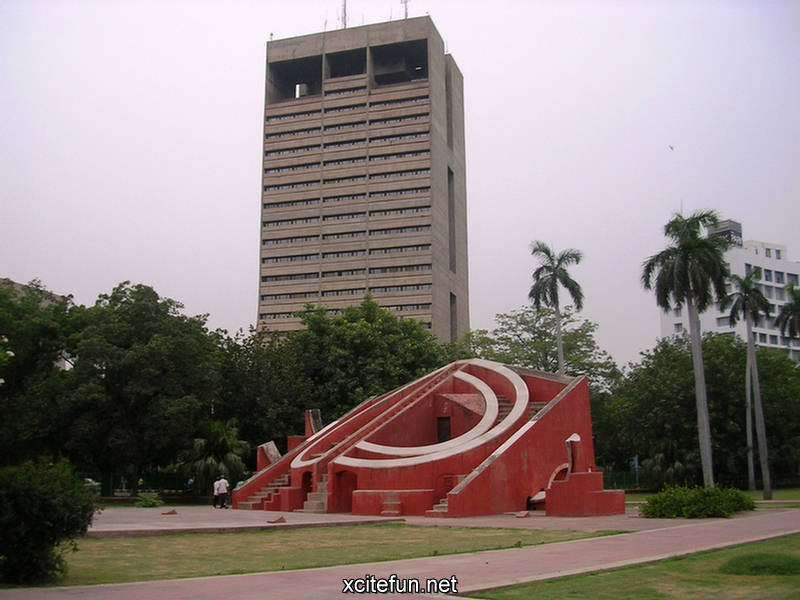
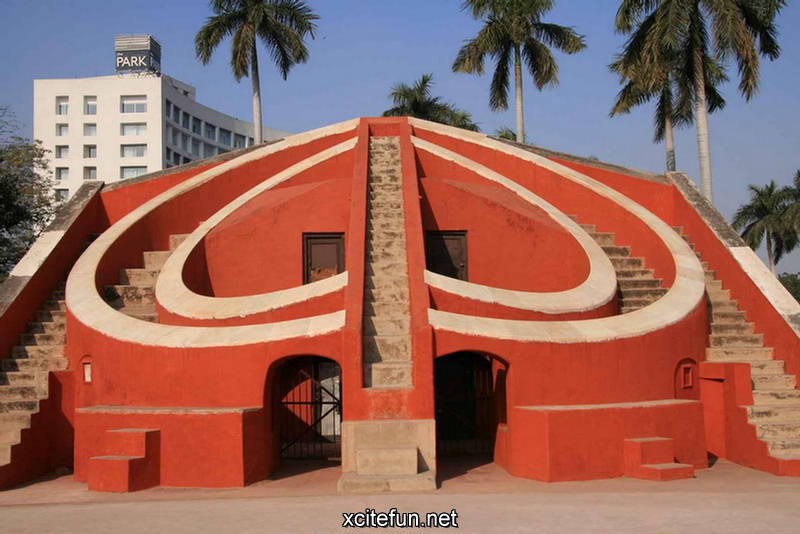
Jantar Mantar Park was built in 1724 under the orders of emperor Muhammad Shah to observe the Sun, Moon and the Stars and compile astronomical tables and charts. Jai Singh invented brass instruments for calculating astronomical values and later replaced them with instruments made of brick, lime and clay. Jantar Mantar is situated in Connaught Place, bang opposite Park Hotel and NDMC building, New Delhi.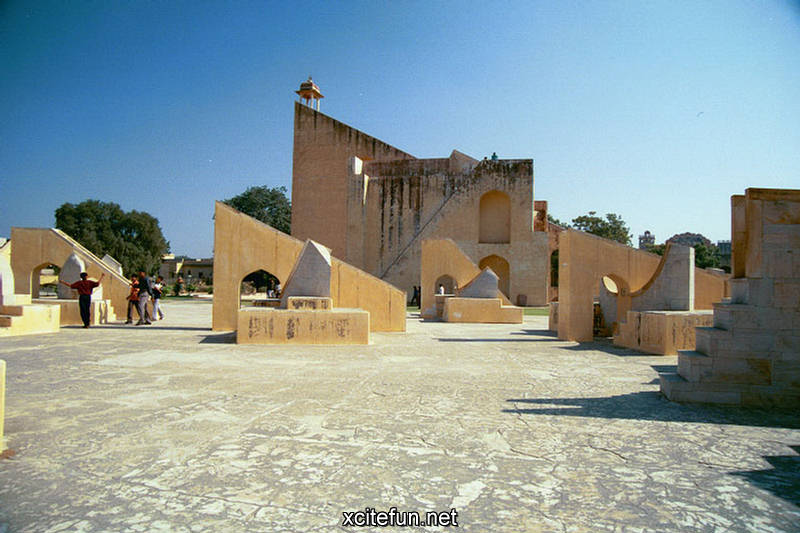
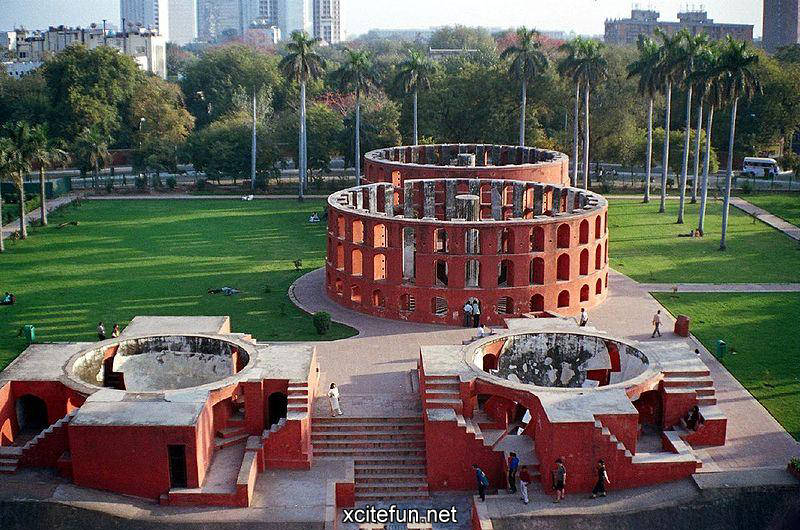
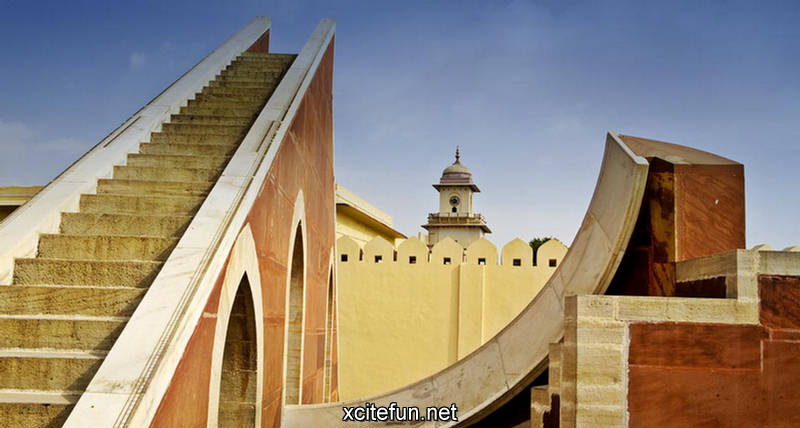
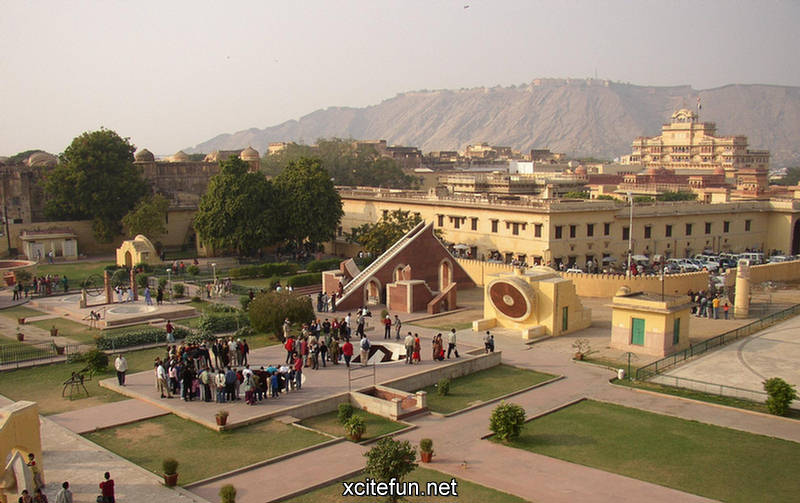
It is part of a group of five stone astronomical observatories, the other ones being constructed at Jaipur, Ujjain, Varanasi and Mathura. The observatory gives a good insight into the technological innovations of the time and is an integral part of India's scientific heritage.
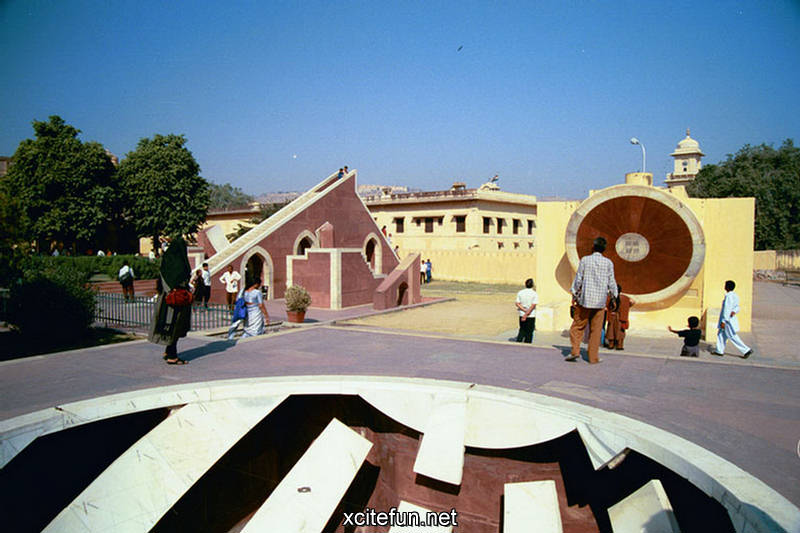

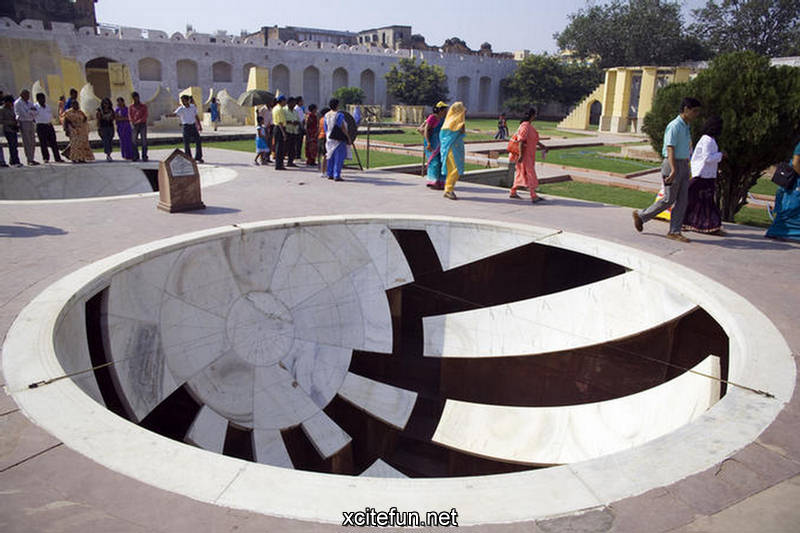
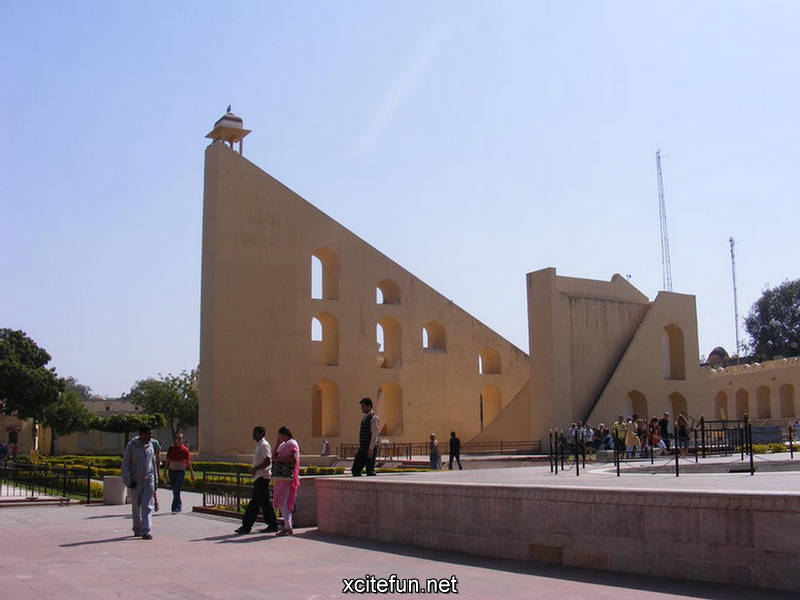
Jantar Mantar is constructed entirely of stone because Jai Singh hated metal observatories. It has six astrological instruments, namely: Samrat Yantra, Jai Prakash Yantra, Niyata Yantra, Ram Yantra, Misra Yantra and Agra Yantra. The one in Delhi is today the largest and most preserved observatory amongst others, though the one is Jaipur is built on a larger scale. Till date the instruments have predicted accurately with a 10 % error margin.
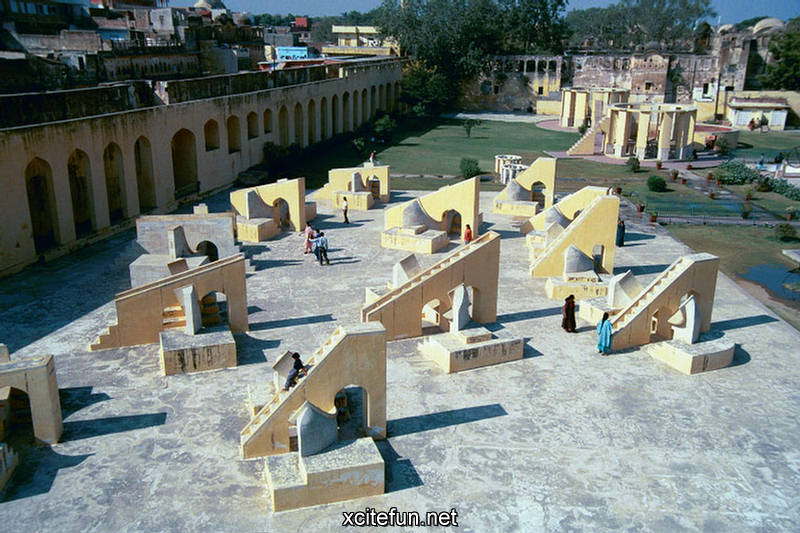
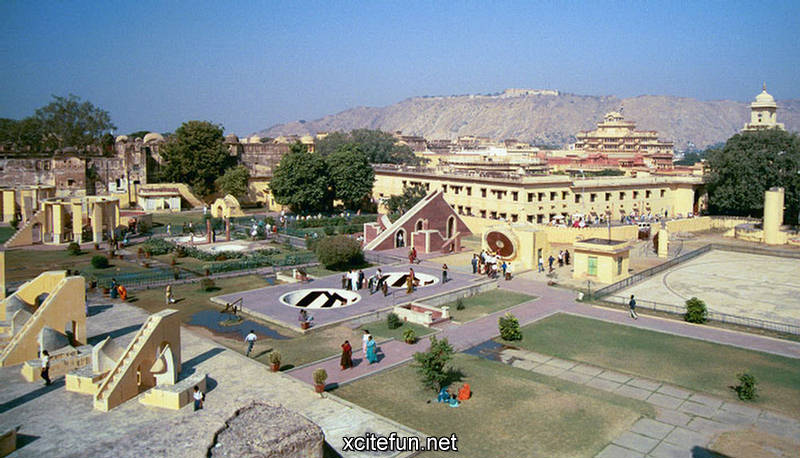















Jantar Mantar Astronomy Park - Visual Tour