Linux Mint is an operating system for personal computers, focusing on elegance. While Mint is mostly based on (and compatible with) Ubuntu, the design of the user interface is considerably different. These differences include:
- A distinct user interface, including a simplified bootloader, desktop layout, theme, and the custom Mint menu.
- Installation of plugins required to play common media formats out of the box
- The Mint Tools, a collection of system tools designed to make system management and administration easier for end users.
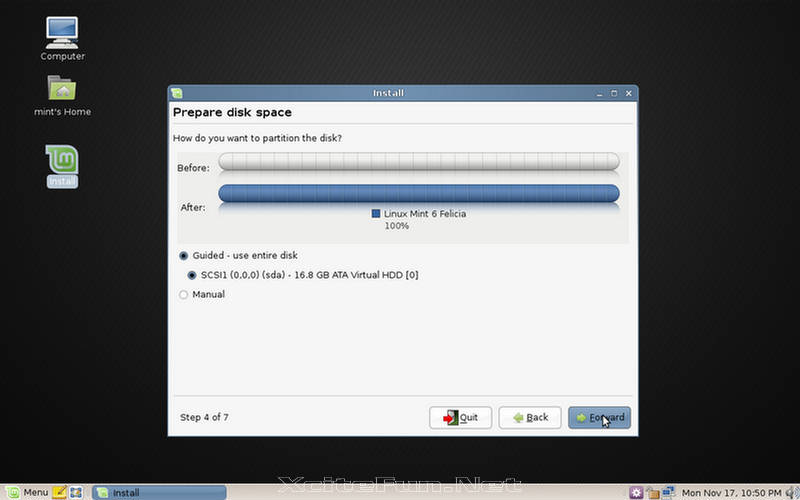
Linux Mint is available for download in the form of ISO images, which can be used to create Live CDs or Live USBs. The latter can be created either manually or using UNetbootin.
Like many other Linux distributions, Linux Mint is available in different test versions or "branches". The branch with the newest features, or "unstable branch" of Linux Mint, is called "Romeo". It is not activated by default in Linux Mint releases. Users who wish to get cutting-edge features and help the distribution test new packages can add Romeo to their Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) sources.
New packages are first released in "Romeo", where they are tested by developers and community members who use it. After a package is found to be stable enough, it is backported to the latest stable release.
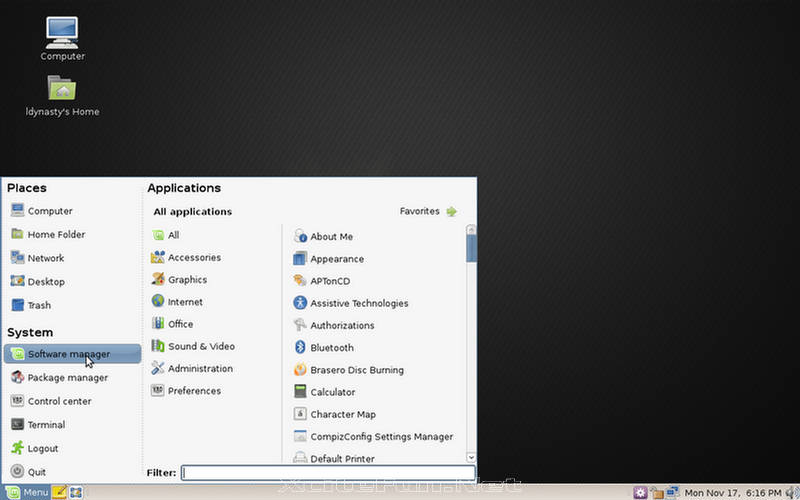
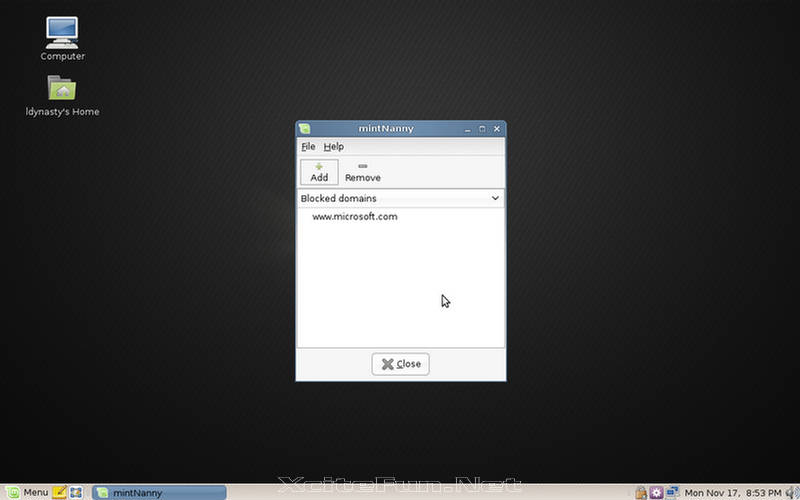
Linux Mint comes with its own set of tools aimed at making the experience easier for the user.
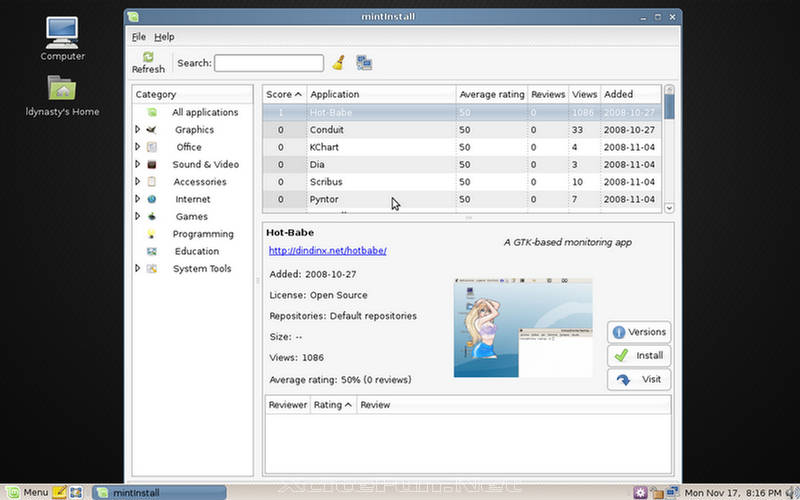
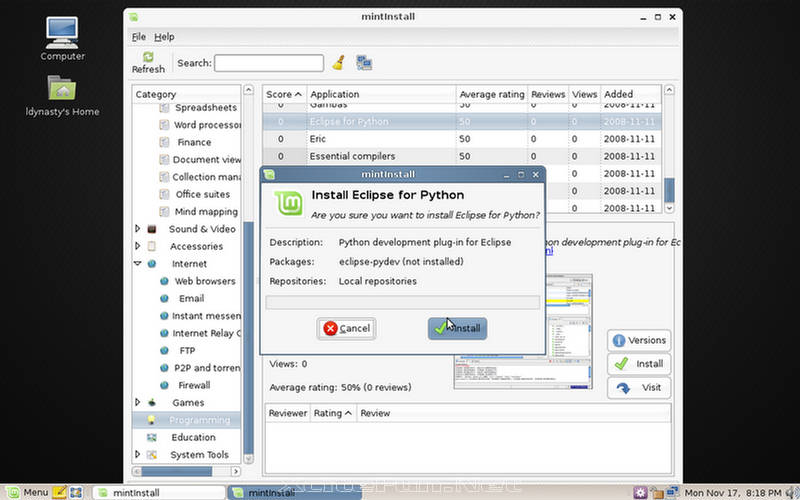
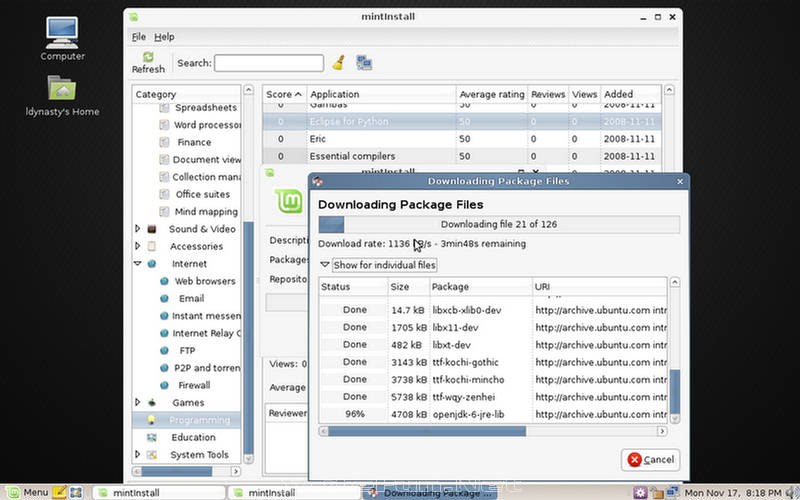
- MintInstall: A program to download software from Internet catalogs that distributes mint-files. A mint-file does not contain the software, but it contains all the information and sources to download that software. mintInstall allows users to add software through the use of .mint files.
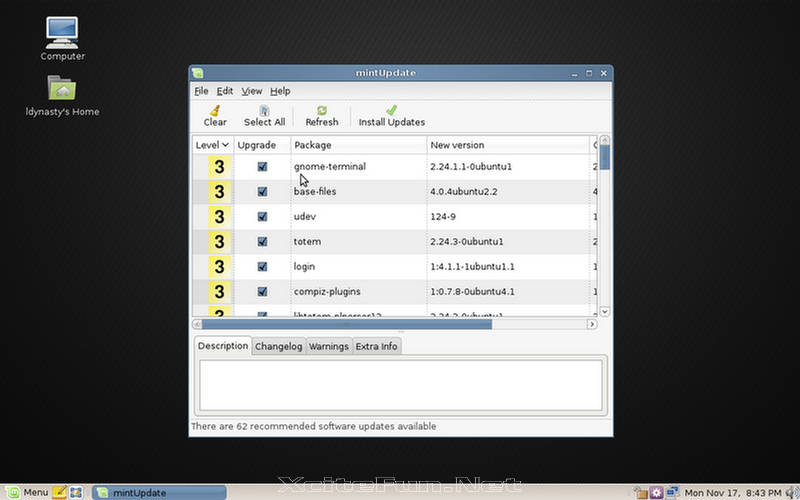
- MintUpdate: Update-software designed specifically for Linux Mint. MintUpdate assigns updates a safety-level (from 1 to 5), based on the stability and necessity of the update. Updates can be set to notify users (as is normal), be listed but not notify, or be hidden by default. In addition to including updates specifically for the Mint distribution, the development team tests all package-wide updates. This system is designed to prevent inexperienced users from installing updates that are unnecessary or require a certain level of knowledge to configure properly. MintUpdate is currently in beta 1.5 and will be included in the next Mint release. If mintInstall is used to install a program from the default repositories, that program is able to receive updates via mintUpdate.
- MintDesktop: A desktop configuration tool for easy configuration of the Gnome desktop. Also acts as a background process to do various tasks upon login. Also network browsing is made easier (through fusesmb). MintDesktop has received a major overhaul in Mint 4.0.
- MintConfig: (Obsolete from Daryna.) A customizable control center. It gathers all the tools from "Preferences" and "Administration" and organizes them into categories. The purpose of mintConfig was to give users a control center since Gnome didn’t have one. In Daryna only the Gnome Control Center is present.
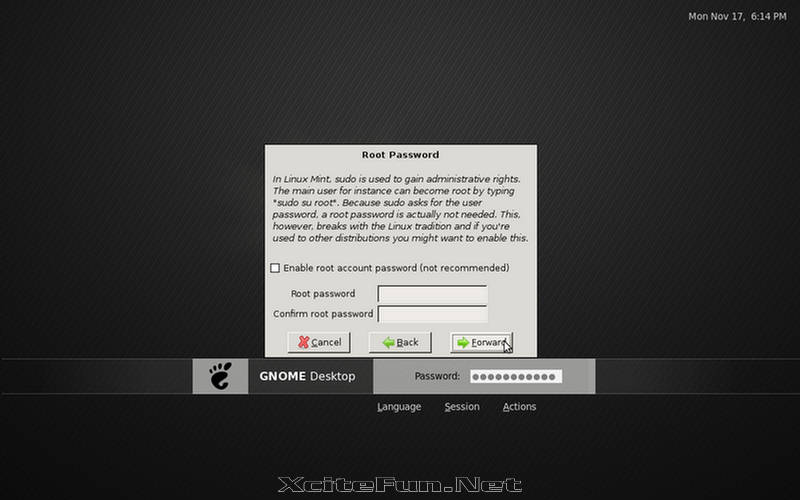
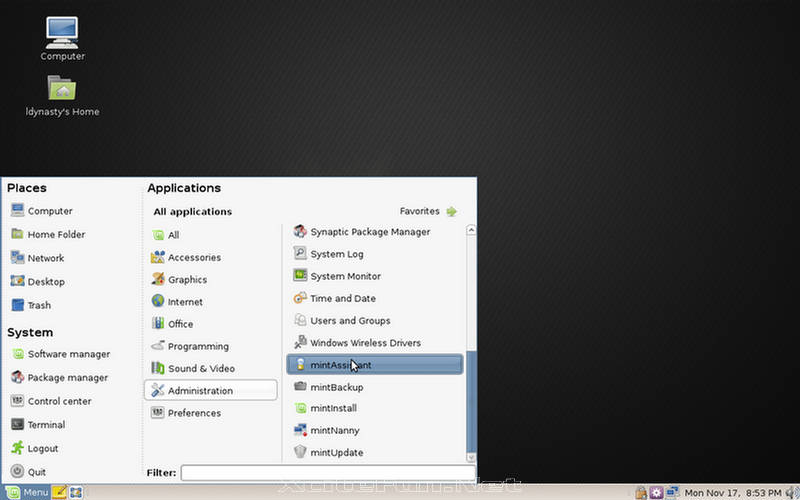
- MintAssistant: A customization wizard that appears during first log-in for users, asking a few questions to customize Mint based on the user's level of knowledge and comfort with various Linux components. It currently asks if the user wants to enable or disable fortune-cookies in the terminal, and if the root account should be enabled or disabled.
- MintUpload: An FTP client that uploads files to a server by right-clicking on the icons and selecting upload. The user will then be given a link he or she can give to other people for quick and easy sharing.
- MintSpace: The larger sibling of MintUpload. Provides an additional 1GB of storage space and files stay on the server for 7 days (rather than 2 days).
- MintMenu: A python-coded menu that allows for fully customizable text, icons, and colors. It shares the same hotlinks to software as the Gnome main menu.
- MintWifi: drivers for quite a few wlan gadgets and mintWifi.py . Located in /usr/lib/linuxmint/mintWifi
Software from the Mint repositories can be installed in Debian and Ubuntu as well through APT.