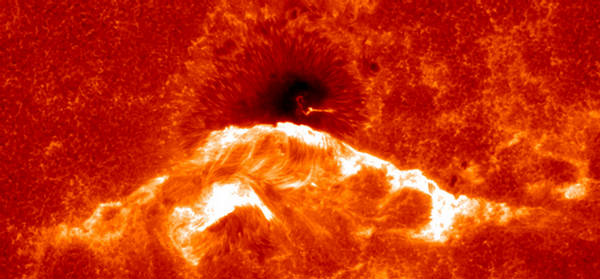
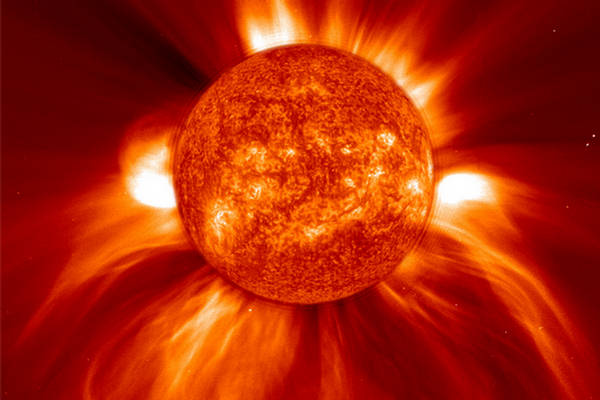
A sweeping prominence, a huge cloud of relatively cool dense plasma is seen
suspended in the Sun's hot, thin corona. At times, promineces can erupt,
escaping the Sun's atmosphere. Emission in this spectral line shows the upper
chromosphere at a temperature of about 60,000 degrees K (over 100,000
degrees F). Every feature in the image traces magnetic field structure. The
hottest areas appear almost white, while the darker red areas indicate cooler
temperatures. (Courtesy of SOHO/EIT consortium)
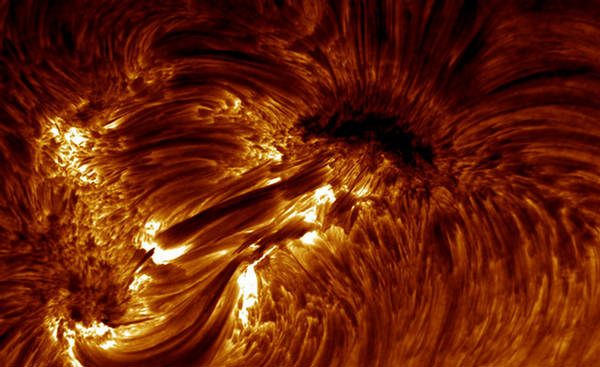
2
Detailed closeup of magnetic structures on the Sun's surface, seen in the
H-alpha wavelength on August 22, 2003. (Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (SST)
operated by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Oddbjorn Engvold, Jun
Elin Wiik, Luc Rouppe van der Voort) #

3
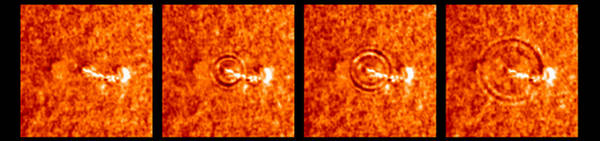
NASA's STEREO satellite captured the first images ever of a collision between
a solar "hurricane", called a coronal mass ejection (CME), and a comet on April
4, 2007. The collision caused the complete detachment of the comet's plasma
tail. Comets are icy leftovers from the solar system's formation billions of
years ago. They usually hang out in the cold, distant regions of the solar
system, but occasionally a gravitational tug from a planet, another comet, or
even a nearby star sends them into the inner solar system. Once there, the
sun's heat and radiation vaporizes gas and dust from the comet, forming its
tail. Comets typically have two tails, one made of dust and a fainter one
made of electrically conducting gas, called plasma. (NASA/STEREO) #
4
Image of an active solar region taken on July 24, 2002 near the eastern limb
of the Sun. The image highlights the three-dimensional nature of the
photosphere when seen at these large angles. The structures in the dark
sunspots in the upper central area of the image show distinct elevation above
the dark "floor" of the sunspot. The height of the structures has been
estimated by Dr. Bruce Lites of the High Altitude Observatory to be between
200 and 450 km. The smallest resolvable features in the image are about 70
km in size. There are also numerous bright "faculae" visible on the edges of
granules that face towards the observer. (Prof. Goran Scharmer/Dr. Mats G.
Löfdahl/Institute for Solar Physics of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences) #

5
The total solar eclipse of February 16, 1980 was photographed from Palem,
India, by a research team from the High Altitude Observatory of the National
Center for Atmospheric Research. The photograph of the solar corona was
taken with a camera system developed by Gordon A. Newkirk, Jr. This
specialized instrument photographs the corona in red light, 6400 A -- through
a radially graded filter that suppresses the bright inner corona in order to
show the much fainter streamers of the outer corona in the same photograph.
(Rhodes College, Memphis, Tennessee / High Altitude Observatory (HAO),
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR)) #

6
The planet Venus is seen by NASA's TRACE satellite, at the start of its transit
across the sun on June 8, 2004. (NASA/TRACE) #
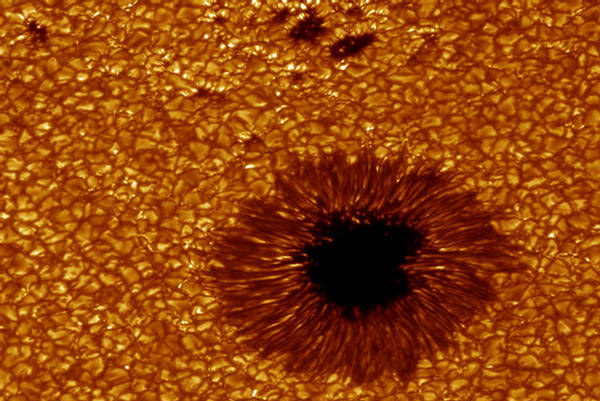
7
A view of a sunspot and granules on the Sun's surface, seen in the H-alpha
wavelength on August 4, 2003. (Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (SST) operated
by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Göran Scharmer and Kai Langhans, ISP) #
8
Solar flares produce seismic waves in the Sun's interior that closely resemble
those created by earthquakes on our planet. On May 27, 1998, researchers
observed this flare-generated solar quake that contained about 40,000 times
the energy released in the great earthquake that devastated San Francisco in
1906, equivalent to an 11.3 magnitude earthquake, scientists calculated.
Over the course of an hour, the solar waves traveled for a distance equal to
10 Earth diameters before fading into the fiery background of the Sun's
photosphere. Unlike water ripples that travel outward at a constant velocity,
the solar waves accelerated from an initial speed of 22,000 miles per hour to
a maximum of 250,000 miles per hour before disappearing. (Courtesy of
SOHO/EIT consortium. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between
ESA and NASA) #
9
An animation of the sun, seen by NASA's Extreme ultraviolet Imaging
Telescope (EIT) over the course of 6 days, starting June 27, 2005. (Courtesy
of SOHO/EIT consortium) #
10
Hinode (formerly known as Solar-B) successfully captured a massive solar
flare on 13 December 2006. It was one of the largest flares occurring in that
period of solar activity minimum. (JAXA/NASA/PPARC) #
11
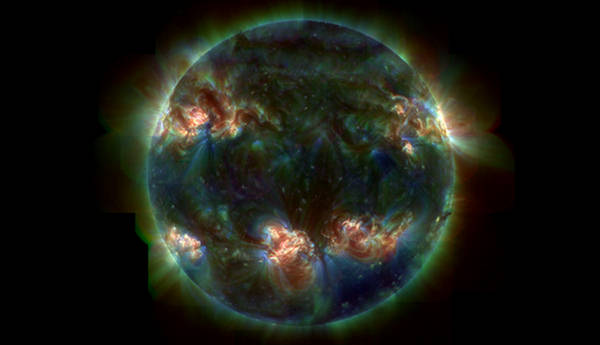
The image shows the corona for a moderately active Sun, with some (red)
hot active regions in both hemispheres, surrounded by the (blue/green) cooler
plasma of the quiet-Sun corona. Notice also the north polar-crown filament,
the trans-equatorial loops, and the coronal hole in the south-east (lower-right) corner of the image and the smaller one over the north pole. This image
shows the solar corona in a false-color, 3-layer composite: the blue, green,
and red channels show the 171Ã…, 195Ã…, and 284Ã… wavelengths, respectively
(most sensitive to emission from 1, 1.5, and 2 million degree gases). (TRACE
Project, Stanford-Lockheed Institute for Space Research, NASA) #
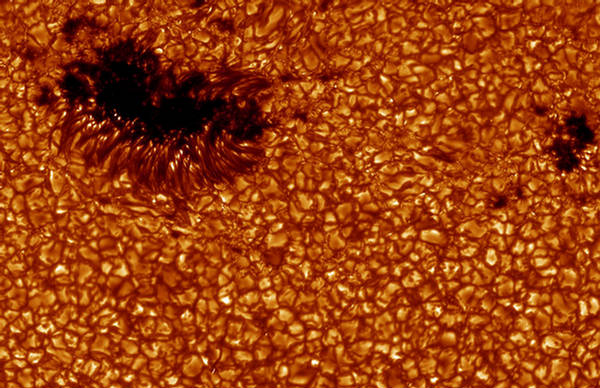
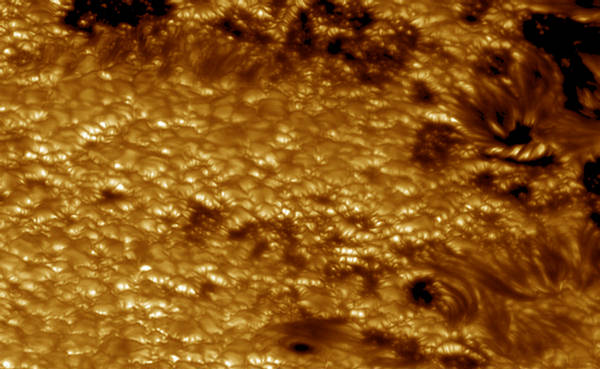
12
A view of an irregular-shaped sunspot and granules on the Sun's surface,
seen on August 22, 2003. (Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (SST) operated by
the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Oddbjorn Engvold, Jun Elin Wiik, Luc
Rouppe van der Voort, Oslo) #
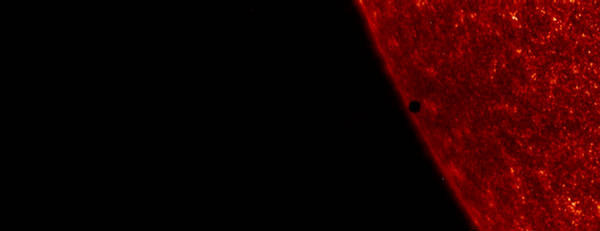
13
On November 8, 2006, Mercury is seen, beginning a transit in front of the
Sun. (NASA/TRACE) #

14
This TRACE 171Ã…-wavelength image from November 11, 2006 shows a sizeable
active region at the east limb of the Sun (rotated clockwise 90 degrees so
north is to the right) just as it rotates onto Earth-facing hemisphere. Notice
the low-lying dark structures of filaments at the leading edge of the region,
some "levitating" dark material on the right-hand side of the region, and the
small ephemeral region towards the lower right. (NASA/TRACE) #

15
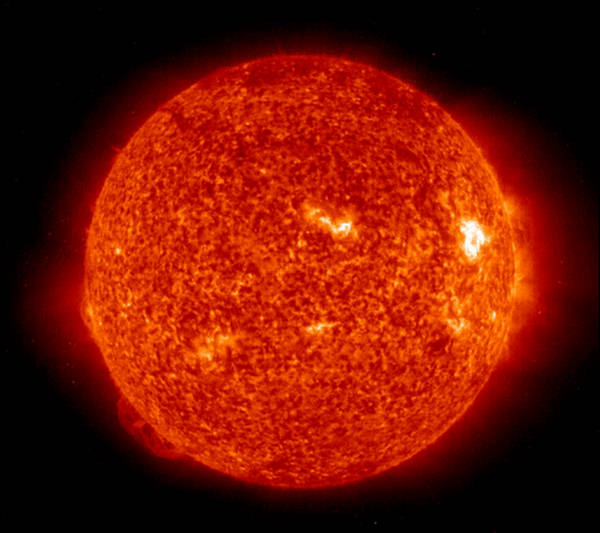
The Sun, observed on May 22, 2008. With the Sun persisting in a
near-minimal state of activity, only a few small regions of some activity are
seen on the disk. The cell-like appearance is formed by the multitude of small
clusters of magnetic flux that are collected in the downflow regions of the
supergranular network of convective motions. (NASA/TRACE) #

16
A display of thin loops is seen arching above active regions of the Sun on
January 1, 2001. (Courtesy Dick Shine, NASA/TRACE) #

17
This LASCO C2 image, taken 8 January 2002, shows a widely spreading
coronal mass ejection (CME) as it blasts more than a billion tons of matter out
into space at millions of kilometers per hour. The C2 image was turned 90
degrees so that the blast seems to be pointing down. An EIT 304 Angstrom
image from a different day was enlarged and superimposed on the C2 image
so that it filled the occulting disk for effect (Courtesy of SOHO/LASCO
consortium) #
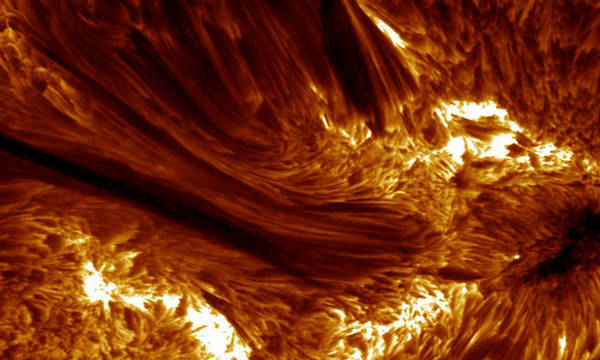
18
Detailed closeup of magnetic structures on the Sun's surface, seen in the
H-alpha wavelength on August 22, 2003. (Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope (SST)
operated by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Oddbjorn Engvold, Jun
Elin Wiik, Luc Rouppe van der Voort, Oslo) #

19
NASA's STEREO (Ahead) spacecraft observed this visually stunning
prominence eruption on Sept. 29, 2008 in the 304 wavelength of extreme UV
light. It rose up and cascaded to the right over several hours, appearing
something like a flag unfurling, as it broke apart and headed into space. The
material observed is actually ionized Helium at about 60,000 degrees.
Prominences are relatively cool clouds of gas suspended above the Sun and
controlled by magnetic forces. (NASA/STEREO) #

20
A transit of the Moon across the face of the Sun on February 25, 2007 - but
not seen from Earth. This sight was visible only from the STEREO-B
spacecraft in its orbit about the sun, trailing behind the Earth. NASA's
STEREO mission consists of two spacecraft launched in October, 2006 to
study solar storms. STEREO-B is currently about 1 million miles from the Earth,
4.4 times farther away from the Moon than we are on Earth. As the result,
the Moon appears 4.4 times smaller than what we are used to. (NASA/STEREO) #
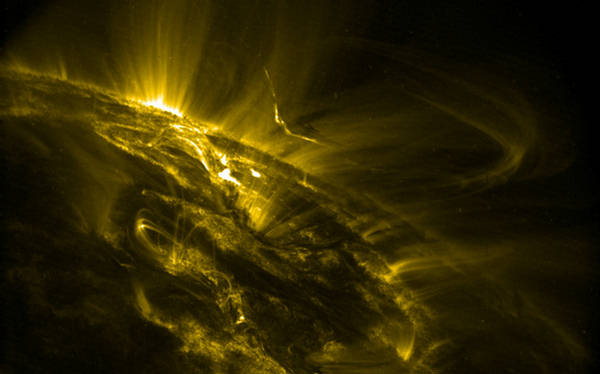
21
On September 30, 2001, TRACE observed an M1.0 flare in an active region
very near to the solar limb. Fragments of a prominence hovered above the
regions, with filamentary dark (relatively cool) material moving along the field
lines, which then spread to form this dragon-like bright outline. (NASA/TRACE)
#