Miscellaneous Photography, Pictures, Wallpapers
-
lovedesire
- Ultimate Contributor
- Posts: 4027
- Joined: Sep 30, 2008
- Location: India
-
Contact:
Post
by lovedesire » Feb 25, 2009 Views: 4353
-
oni
- Fun Addict

- Posts: 771
- Joined: Mar 14, 2007
Post
by oni » Feb 25, 2009
Great one. I have seen the first image all the time. Other close images are good one to share
-
moonjee06
- Extreme Contributor
- Posts: 3162
- Joined: May 26, 2008
Post
by moonjee06 » Feb 25, 2009
love never die
I LOVE S


-
MurXA
- Just Born

- Posts: 7
- Joined: Jan 29, 2009
Post
by MurXA » Mar 06, 2009
this is complete ISlamic state of ART
-
MurXA
- Just Born

- Posts: 7
- Joined: Jan 29, 2009
Post
by MurXA » Mar 06, 2009
this is complete ISlamic state of ART
-
ujala
- Ultimate Contributor
- Posts: 18532
- Joined: Jan 31, 2009
- Location: Islamabad
-
Contact:
Post
by ujala » Mar 06, 2009
Excellent Lovedesire ..................well done great post
As many people watch n know about those place
ll pray 4 u .............
very nice post
-
Pearl
- Ultimate Contributor
- Posts: 8069
- Joined: Mar 30, 2009
- Location: Deep inside the sea
-
Contact:
Post
by Pearl » Apr 20, 2009
Wonderfull
A great gift of love
-
Astir
- The Super Geek
- Posts: 1812
- Joined: Dec 23, 2008
- Location: India(Kerala)
-
Contact:
Post
by Astir » Apr 21, 2009
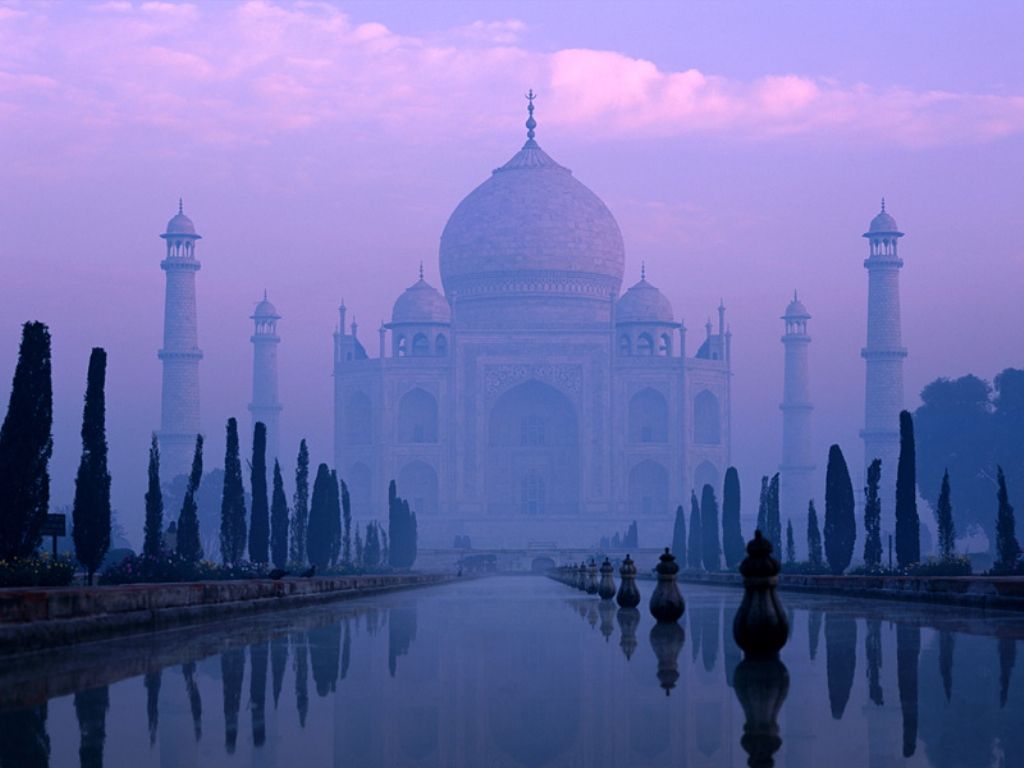
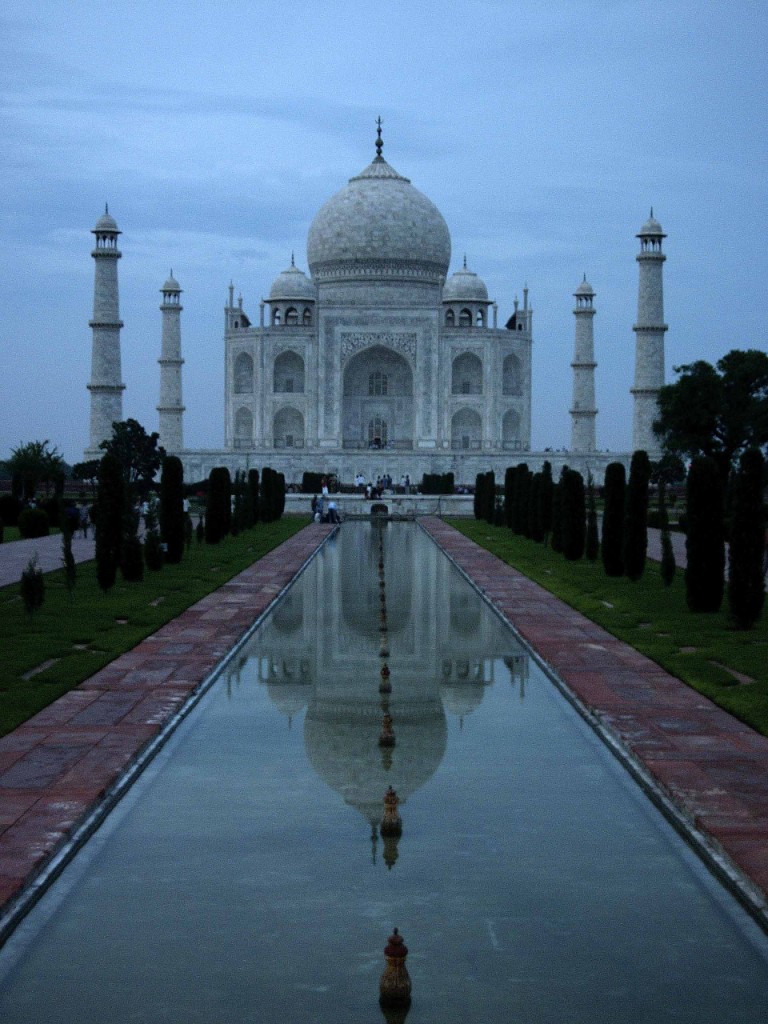
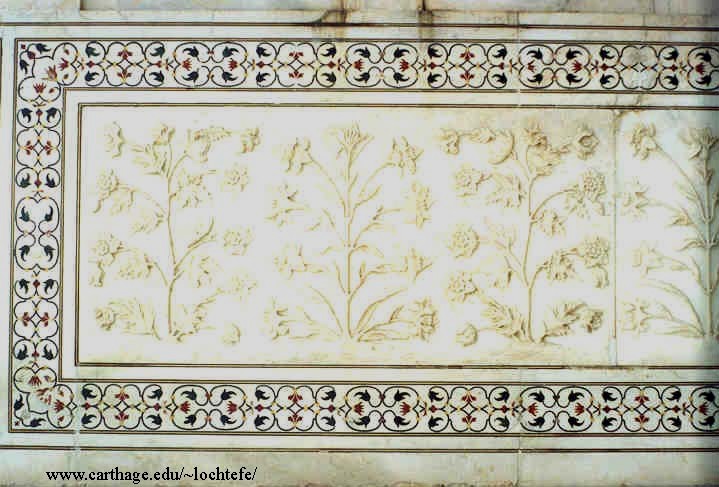
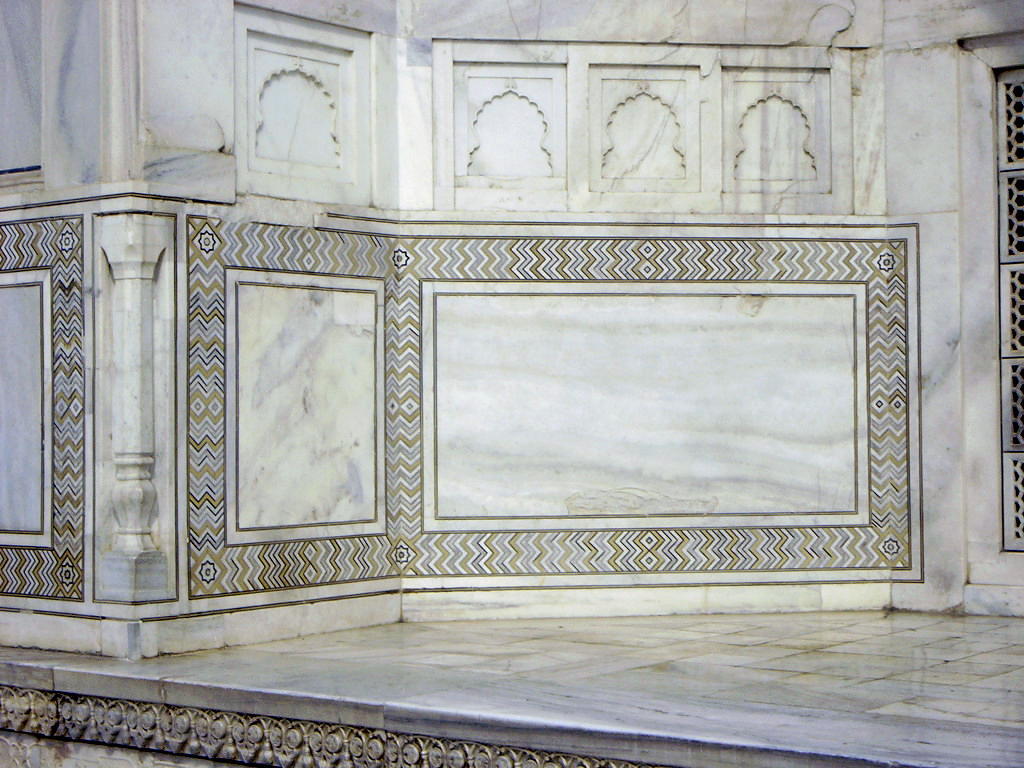
The Taj Mahal (pronounced /tɑdʒ mə'hɑl/ ---- Hindi: ताज महल; Persian/Urdu: تاج محل) is a mausoleum located in Agra, India, built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his favorite wife, Mumtaz Mahal.
The Taj Mahal (also "the Taj") is considered the finest example of Mughal architecture, a style that combines elements from Persian, Ottoman, Indian, and Islamic architectural styles. In 1983, the Taj Mahal became a UNESCO World Heritage Site and was cited as "the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage."
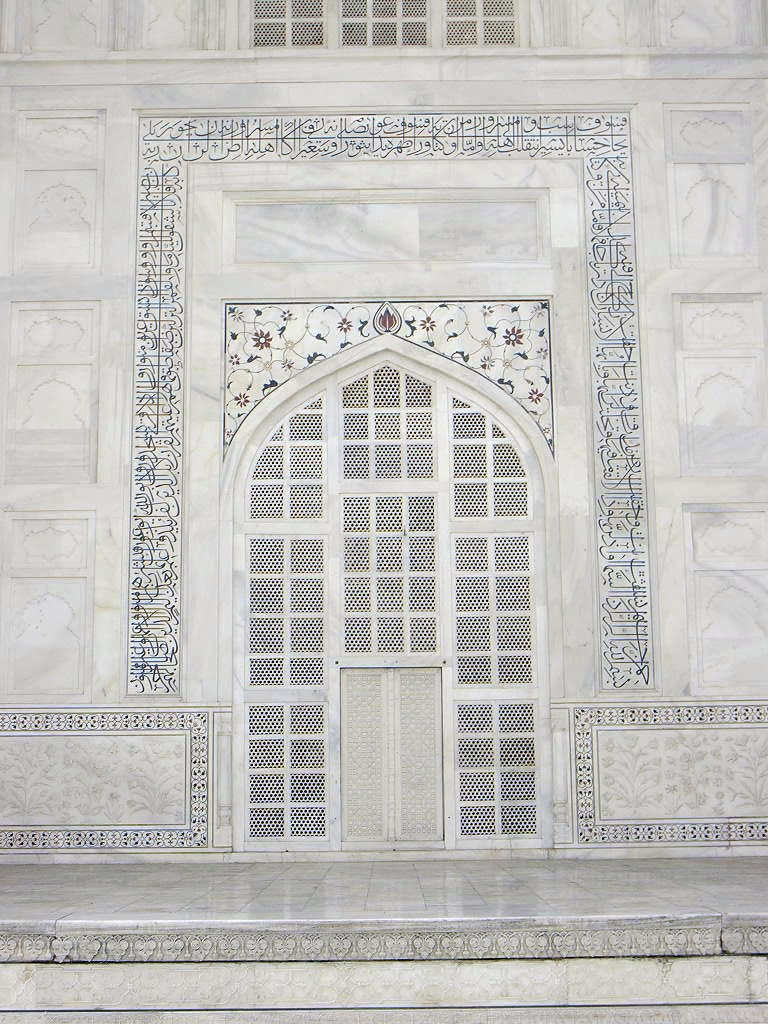
While the white domed marble mausoleum is its most familiar component, the Taj Mahal is actually an integrated complex of structures. Building began around 1632 and was completed around 1653, and employed thousands of artisans and craftsmen.[1] The Persian[2] architect, Ustad Ahmad Lahauri is generally considered to be the principal designer of the Taj Mahal.[3]
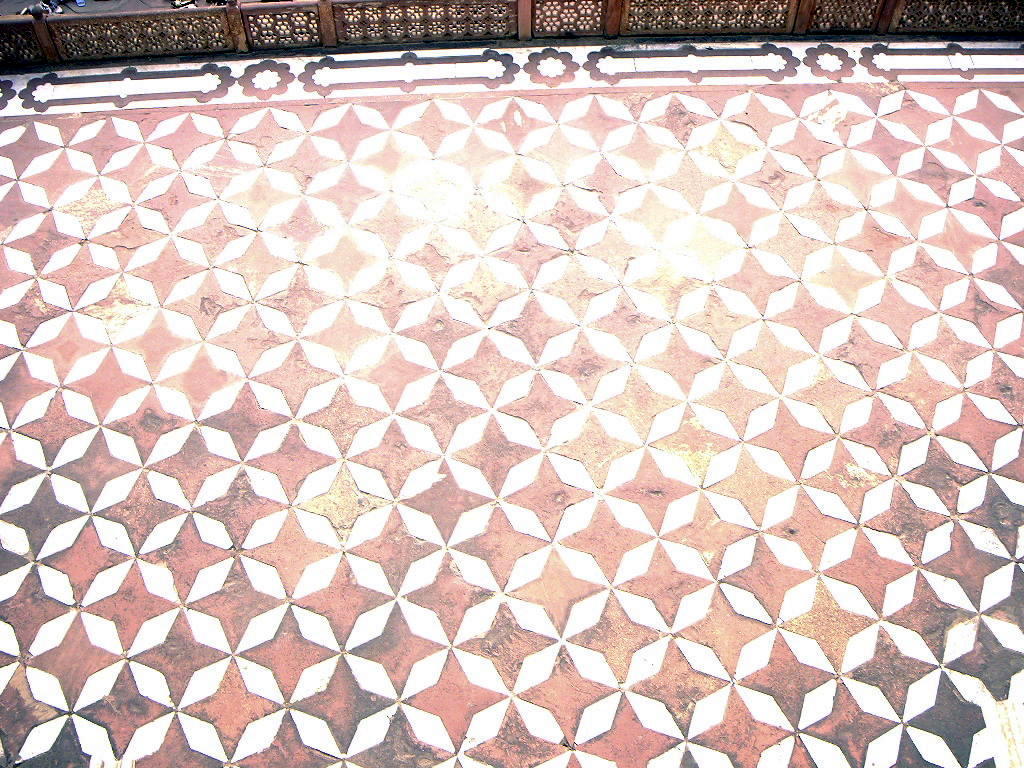
Mughal architecture, an amalgam of Islamic, Persian and Indian architecture, is the distinctive style developed by the Mughal Empire in India & Pakistan in the 16th and 17th centuries.
lamic architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Islam to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Islamic culture. the building show the wealth of the person that lives in it. The principal Islamic architectural types are: the Mosque, the Tomb, the Palace and the Fort. From these four types, the vocabulary of Islamic architecture is derived and used for buildings of lesser importance such as public baths, fountains and domestic architecture.[1][2]
Architecture in "Greater Iran" has a continuous history from at least 5000BCE to the present, with characteristic examples distributed over a vast area from Syria to North India and the borders of China, from the Caucasus to Zanzibar. Persian buildings vary from peasant huts to tea houses, and garden pavilions to "some of the most majestic structures the world has ever seen".[1]
Iranian architecture displays great variety, both structural and aesthetic, developing gradually and coherently out of prior traditions and experience. Without sudden innovations, and despite the repeated trauma of invasions and cultural shocks, it has achieved "an individuality distinct from that of other Muslim countries".[2] Its paramount virtues are several: "a marked feeling for form and scale; structural inventiveness, especially in vault and dome construction; a genius for decoration with a freedom and success not rivaled in any other architecture".[3]

The architecture of India is rooted in its history, culture and religion.[1] Indian architecture progressed with time and assimilated the many influences that came as a result of India's global discourse with other regions of the world throughout its millennia old past.[1] The architectural methods practiced in India are a result of examination and implementation of its established building traditions and outside cultural interactions.[1]
Though old, this Eastern tradition has also incorporated modern values as India became a modern nation state.[1] The economic reforms of 1991 further bolstered the urban architecture of India as the country became more integrated with the world's economy.[1] Traditional Vastu Shastra remains influential in India's architecture during the contemporary era.[1]